What is customer relationship management (CRM) & why should you care?
This article was first published in the downloadable first issue of markonmag. The article has since been updated and expanded upon by Nicole Rachel Kwan.
CRM is the technology-enabled tool used by companies to manage interactions with current and potential customers.
The definition of CRM depends on what you’re thinking of: CRM software, CRM strategy, or CRM processes.
Here’s a short explanation of each:
CRM Software: Salesforce defines it as a platform that combines the info collected from different departments - usually sales, marketing and customer service - into one system. This gives users easy access to client data.
CRM Strategy: high-level guidelines on direct interactions with customers and leads. It is a business strategy that aims to build and maintain relationships with customers by delivering value to them.
CRM Process: a system used by a company to have personalized and meaningful customer interactions.
We’ll get into more detail later, but first —
Why is CRM important?
CRM involves analyzing large amounts of data collected by firms. Based on the insights gathered, companies plan and carry out strategies to improve business relationships with customers, specifically focusing on customer retention and ultimately driving sales growth.
What types of CRM are there?
There are 3 types of CRM, namely, Strategic, Operational, and Analytical.
1) Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM focuses on the development of a customer-centric business culture dedicated to managing and retaining profitable customers by creating and delivering better value than competitors.
Hence, a lot of resources will be allocated to increase customer value. For instance, a company might implement a reward system to encourage front-line employees to provide services that enhance customer satisfaction and retention.
2) Operational CRM
Operational CRM focuses on automating customer-facing business processes – Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service Support.
Customer service automation focuses on the technology via offline and online channels that serve customers such as chatbots, FAQs, emails, and phones.
3) Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM focuses on both internal and external customer data. Internal customer data is captured and processed through sales data (eg. purchase history), financial data (eg. payment history, credit score), marketing data (eg. campaign response, loyalty scheme data), and service data (eg. previous customer support tickets).
For external data, companies use data from other business intelligence organizations to capture geo-demographic and lifestyle data of their customers.
With all the data collected, data mining tools will be used to interrogate this data to answer questions such as “Who are the most valuable customers?”, “Which customer is more likely to churn?” and “Who will have the most positive reaction to this marketing campaign?”.
What is the customer relationship management process like and what does it involve?
The CRM process is a system that aims to keep customer interactions meaningful and personalized. It runs in parallel with the customer lifecycle, beginning from awareness all the way to loyalty.
Here are the five stages:
1. Awareness
The first step is getting customers to find out about your brand, i.e. generating brand awareness. This is usually done by the marketing team through marketing campaigns.
How CRM helps: CRM software stores all the information on customers and leads. Marketers can use this data to gain a deeper understanding of their target audience, which helps with the development of more effective campaigns.
2. Acquisition
Next in the process is lead acquisition: encouraging potential customers to learn more about and engage with your brand. Depending on your company, it could be done either by sales or marketing.
For example, a sports equipment brand’s marketing team might encourage newsletter sign-ups with a 10% discount. On the other hand, a software service provider might offer a free trial after a demo call with a salesperson.
How CRM helps: Data collected from these leads — email addresses, phone numbers, locations — can be stored in the CRM and saved for future use. Forms can be created on the CRM system itself and plugged into the website.
3. Conversion
Now that you have a group of leads, the next step is to encourage them to make a purchase. Again, depending on your company, this can be done by sales or marketing.
A B2B business might have salespeople send more resources, or develop a special sales offer for the lead. For a B2C retail store, marketing might send unique sales newsletters or discount codes.
How CRM helps: Salespeople can score leads according to their intent to buy, or view their purchase history. In addition, emails to leads can be automated. We’ll talk more about this later 😉.
4. Retention
Congratulations! The customer decided to make a purchase 🎉
… Now what?
It’s time to continue building the relationship you’ve begun with the customer, through excellent customer support!
As my professor used to say when I took CRM as a marketing elective in SMU, every touchpoint with your customer is a chance to delight them. It’s essential that companies continue to deliver positive experiences to customers so that they want to come back.
How CRM helps: Customer support staff can use the information stored in the CRM software to quickly resolve the issues that the customer is facing, without having to ask. This reduces the friction and stress experienced by both the customer and agent.
5. Loyalty
Last in this cycle is customer loyalty - encouraging continued purchasing through upselling and cross-selling. Depending on your business, this might be in the form of service level upgrades, or selling them a handbag to match their new shoes.
How CRM helps: The CRM stores data on past purchases, which can help companies figure out which products or services might be of interest to their customers. Customers with similar interests can be grouped together, and emails promoting these products or services can be automated.
What do CRM systems do?
1. Customer Data Management
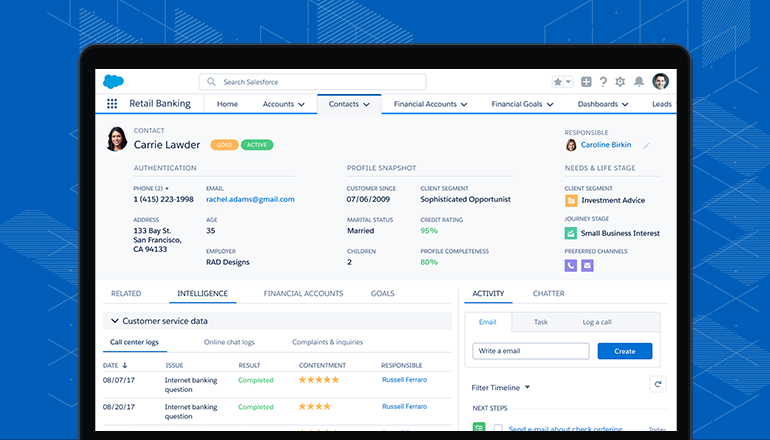
Salesforce CRM’s customer data management feature allows you to keep track of all customer information.
CRM software store all the data about your customer in a single location, allowing relevant parties to easily access the information they need. Typical forms of information that a CRM software may store are:
Contact information: phone numbers, email addresses, mailing addresses, and such.
Communication history: previous touchpoints with the customer, such as emails, phone calls, or online chats.
Customer history: how long they’ve been your customer, their purchase history, subscription renewal schedules, etc.
Having all the data stored in one location keeps everyone working with the latest information. This results in a more organized effort by keeping everyone updated and on the same page about where a lead is in the process.
2. Marketing Campaign Management
CRM systems offer campaign management features, helping marketers to keep track of their process. Marketers can use the data collected about customers to segment them into different groups according to chosen characteristics.
Hubspot CRM’s marketing automation feature allows you to create automated email sequences.
For example, a health and nutrition company might create one email campaign promoting protein powder for those who purchased sports-related wellness products, and a separate campaign promoting vitamins for those who bought health supplements.
CRM systems can also help with ad campaign reporting and optimization. They can track actions such as link clicks, or message opens.
For example, Hubspot CRM lets you build your campaign by connecting ad accounts, and bringing ad analytics from different ad platforms into one platform for management and optimization.
3. Sales Process Automation
Some CRM software, such as Salesforce, allows you to build sales processes and workflows. They also allow automation of routine tasks.
Zoho (and many other CRM systems) has a workflow automation feature that automatically performs tasks when a trigger event occurs. For example, a workflow can be set up to send a confirmation email (the task) when an order form is submitted successfully (the trigger event).
The automation offered by CRM systems reduces time wasted on less important items. This allows employees to spend time on higher-priority tasks.
Types of CRM software
1. Hosted / Cloud-based
In a hosted CRM system, companies have access to the software via an internet connection. The CRM vendor, such as Salesforce, stores and maintains the data.
This type of system has its pros and cons: while not having to maintain servers, hardware and security reduce the costs to the company, cloud-based CRM systems pose some security concerns from having data stored in the cloud.
2. On-premise
As you can guess, on-premise CRM has data stored in on-site servers. The company itself maintains and owns all the information, and software is installed on the company’s PCs.
Compared to cloud-based CRM software, on-premise CRM tends to be more secure as the company has control over physical servers and security measures. In-house IT staff are responsible for any updates that need to be made, so there's more flexibility in terms of timing.
What was working as a CRM marketer like?
A CRM marketer focuses on building value-based relationships in a systematic and productive manner, hence CRM involves some market research and analysis of customers.
CRM marketers spend much time acquiring in-depth knowledge and market trends relating to their customers through various databases and external resources.
However, it is also vital to communicate and deal with customers as well.
Thus, daily on-site visits to speak with different stakeholders (such as suppliers, frontline staff, and customers) are essential to build rapport and establish good customer relationships.
What are the necessary skills to acquire?
1. Meticulous and detail-oriented
Applicable to many other jobs, being detail-oriented is essential in CRM. As mentioned above, every interaction is judgment day - you wouldn’t want your email to go to the wrong audience set!
2. Data analytics
Data Analytics skills (Excel – Pivot table, Vlookup etc): Some basic analysis skills are needed, considering that you’ll be working with lots of information and data. You should also be able to understand and use relevant customer market trends in the data analysis.
3. Working knowledge of the various CRMs
CRM software such as Salesforce or its alternatives like Oracle: having some working knowledge of a CRM system is a plus. Even if you haven't used one before, some platforms like Salesforce have free training programs that teach you some CRM basics.
Of course, these are just some of the skills you need to be a good marketer.
Wrapping up
Well, that was a lot of information.
In sum, CRM is a colorful world built on customer data. With the help of modern CRM systems, marketers can craft more effective campaigns, which increase the value provided to the customer.
Interested in learning more about the different fields of marketing? Check out the rest of our articles in this free marketing magazine!